+86-0572-5888031
How to Use the Ergonomic Chair Correctly
 2025.11.21
2025.11.21
 Industry News
Industry News
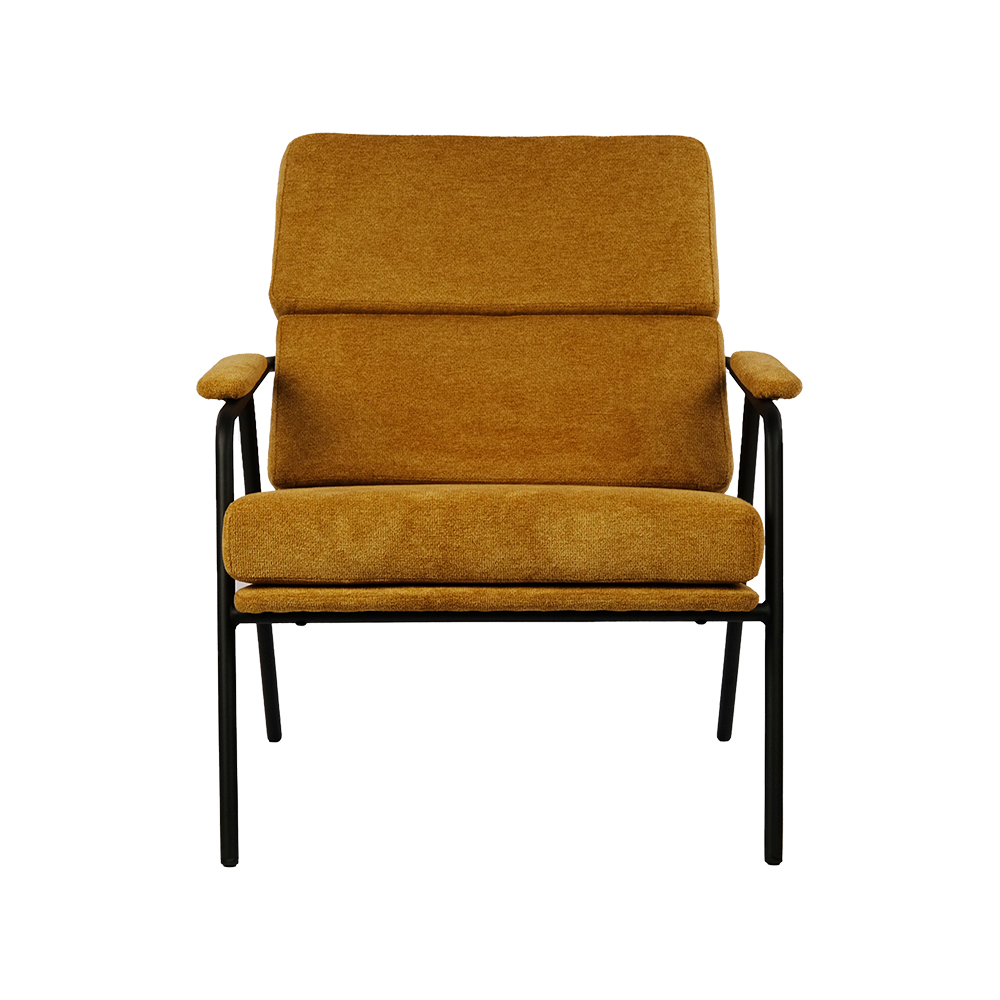
In today’s world, where many of us spend hours sitting at desks, the importance of proper seating cannot be overstated. An Ergonomic Chair is designed to support the natural curve of the spine, promote good posture, and reduce strain on muscles and joints. However, simply having an Ergonomic Chair is not enough. Using it correctly is crucial to experience its full benefits and prevent discomfort or injury.
Understanding the Ergonomic Chair
An Ergonomic Chair differs from standard office chairs in several key ways. It typically includes adjustable features such as seat height, backrest tilt, lumbar support, armrests, and sometimes even seat depth. These features are designed to accommodate different body types, work habits, and postures, helping to reduce fatigue and prevent musculoskeletal problems.
Before learning how to use it, it’s important to understand the main components of an Ergonomic Chair:
- Seat Height Adjustment – Allows your feet to rest flat on the floor, with knees at roughly a 90-degree angle.
- Lumbar Support – Supports the lower back’s natural inward curve. Proper lumbar support prevents slouching.
- Backrest Tilt and Recline – Enables movement and reduces pressure on the spine.
- Armrests – Supports the arms while reducing strain on shoulders and neck.
- Seat Depth Adjustment – Ensures proper thigh support and circulation.
Knowing these components will help you adjust the chair to your body and working style.
Step 1: Adjusting Seat Height
Proper seat height is the foundation of correct Ergonomic Chair use. To adjust:
- Sit on the chair and place your feet flat on the floor.
- Your knees should form roughly a 90-degree angle, with thighs parallel to the ground.
- If your chair has a pneumatic height adjustment lever, raise or lower the seat until this position is achieved.
Avoid sitting too high, as this can strain your thighs and reduce circulation. Sitting too low can lead to slouched posture and back discomfort.
Step 2: Setting Lumbar Support
The lower back is particularly vulnerable during prolonged sitting. Most Ergonomic Chairs come with adjustable lumbar support. To set it correctly:
- Locate the lumbar support adjustment (often a knob or sliding mechanism).
- Position it so that it fits the inward curve of your lower spine.
- Sit back fully against the backrest to ensure the support is in contact with your lower back.
Proper lumbar support helps maintain the natural spinal curve, preventing slouching and reducing pressure on intervertebral discs.
Step 3: Adjusting the Backrest
A backrest that is too upright or too reclined can cause strain over time. Follow these steps for correct adjustment:
- Set the backrest to support the full length of your spine, ideally following its natural S-shape.
- A slight recline of about 100–110 degrees is often recommended to reduce lumbar stress.
- Ensure your shoulders remain relaxed and your chest open while leaning back.
Avoid locking the backrest in one fixed position for hours. Micro-movements and small adjustments throughout the day improve circulation and reduce stiffness.
Step 4: Setting the Armrests
Armrests support your arms, reducing strain on shoulders and neck. To adjust armrests properly:
- Set the armrest height so your shoulders are relaxed and elbows are bent at roughly 90 degrees.
- Adjust the width (if possible) to allow your elbows to rest comfortably without spreading your arms too far apart.
- Ensure your forearms can rest lightly on the armrests while typing or using a mouse, without lifting your shoulders.
Avoid letting your arms dangle or resting on armrests that are too high, as this can lead to shoulder tension.
Step 5: Adjusting Seat Depth
Seat depth adjustment ensures that your thighs are supported without pressure on the back of your knees. To adjust:
- Sit fully back in the chair.
- Ensure there is a small gap (approximately 2–3 inches or 5–8 cm) between the edge of the seat and the back of your knees.
- Adjust the seat depth if your chair allows, so your thighs are supported without restricting circulation.
Proper seat depth promotes comfort during long periods of sitting and helps maintain good posture.

Step 6: Positioning Your Desk and Monitor
Even the best Ergonomic Chair cannot fully compensate for poor desk setup. For correct posture:
- Your monitor should be at eye level, about 20–30 inches (50–75 cm) away.
- Keep your keyboard and mouse at a height that allows elbows to remain at 90 degrees, close to your body.
- Avoid leaning forward or twisting your body to reach equipment.
The combination of a well-adjusted Ergonomic Chair and an appropriately set workspace maximizes comfort and efficiency.
Step 7: Practicing Good Sitting Habits
Even with perfect chair settings, prolonged static sitting can still cause discomfort. Follow these tips:
- Take short breaks every 30–60 minutes to stand, stretch, or walk.
- Shift your position slightly throughout the day to prevent stiffness.
- Engage your core muscles lightly to maintain upright posture.
- Avoid crossing your legs for long periods, as this can reduce circulation.
These small habits, combined with a properly adjusted Ergonomic Chair, significantly reduce the risk of musculoskeletal problems.
Step 8: Maintenance and Care
To ensure your Ergonomic Chair continues to provide support:
- Periodically check that all adjustments and bolts are secure.
- Clean the chair according to its material specifications (mesh, fabric, or leather).
- Inspect for wear and tear, especially in lumbar support and armrest padding.
Regular maintenance helps prolong the chair’s lifespan and keeps it functioning as intended.
Conclusion
Using an Ergonomic Chair correctly involves more than just sitting down. Proper adjustments of seat height, lumbar support, backrest, armrests, and seat depth, combined with a well-organized workspace and good sitting habits, are essential for preventing pain, improving posture, and maintaining comfort during long hours of work. By investing a few minutes in setting up your chair and practicing mindful sitting, you can make a significant difference to your overall health and productivity.
A correctly used Ergonomic Chair is an ally in maintaining a healthier, more comfortable workday. Remember, even the best chair cannot replace movement—frequent breaks, stretches, and attention to posture are equally important. With the right setup and habits, your Ergonomic Chair can help you work smarter, not just longer.

 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español 中文简体
中文简体